As Africa seeks to unlock its economic potential and provide reliable electricity to millions, solar energy is emerging as a key enabler. With over 600 million people lacking access to electricity, especially in Sub-Saharan Africa, solar power offers a scalable, cost-effective, and environmentally sustainable solution.
Why Solar, Why Now? ⚡
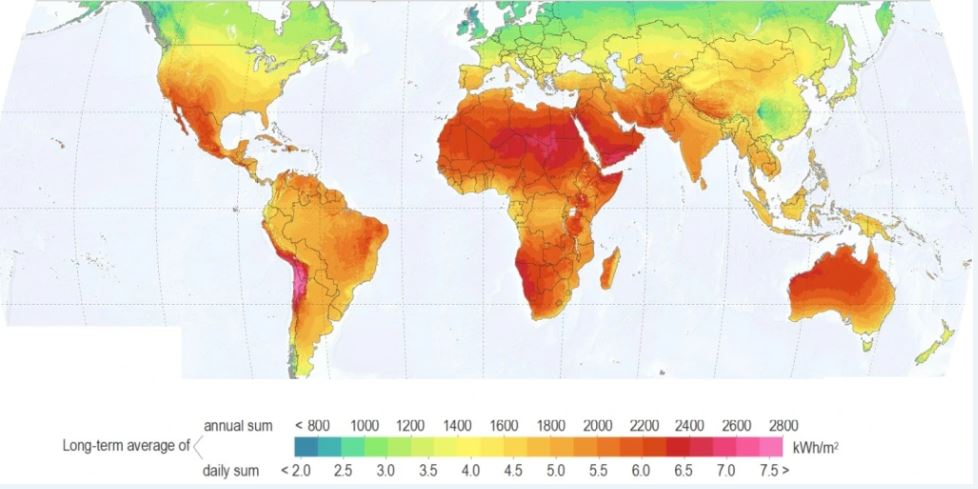
Africa is uniquely positioned to benefit from solar energy. The continent receives some of the highest solar irradiation levels globally, with many regions averaging over 2,000 kWh/m² annually. The declining cost of photovoltaic (PV) technology, coupled with increasing investor appetite for green infrastructure, makes solar not only viable but also highly competitive.
From mini-grids powering remote communities to utility-scale plants supporting national grids, solar projects are diversifying Africa’s energy mix and reducing dependency on fossil fuels.
Financial Modelling: A Cornerstone of Bankability 📊
Robust financial modelling is critical in securing financing for solar projects. Investors and lenders require confidence in a project’s financial viability, risk exposure, and return profile. Key components include:
- Project IRR and NPV: Evaluating the long-term profitability and value creation.
- Tariff structures and PPA terms: Modelling revenue stability under different pricing mechanisms.
- Debt structuring and DSCR analysis: Balancing equity and debt to optimise returns while maintaining acceptable risk levels.
- Scenario and sensitivity analysis: Accounting for variables like currency fluctuation, policy changes, and solar yield variability.
Finteam provides a Solar PV Model Template tailored for African markets, available here: Finteam Solar PV Model Template on Eloquens.
Case Studies Across the Continent 🌍
- South Africa: Home to one of the continent’s most advanced renewable energy procurement programmes (REIPPPP), the country has commissioned over 2 GW of solar capacity.
- Nigeria: Through the Nigeria Electrification Project (NEP), solar mini-grids are being deployed to connect rural communities, supported by World Bank and AfDB funding.
- Morocco: The Noor Ouarzazate Solar Complex is among the world’s largest, showcasing the potential for concentrated solar power (CSP) in North Africa.
- Kenya and Uganda: Utility-scale PV projects such as the Garissa Solar Plant and Tororo Solar North are adding much-needed capacity to national grids.
Key Enablers for Success 🌱
To scale solar adoption, several factors must align:
- Policy and Regulatory Stability: Clear, consistent frameworks reduce investment risk.
- Access to Concessional Finance: Blended finance structures can unlock private sector capital.
- Local Capacity Building: Training local engineers, developers, and financiers ensures long-term sustainability.
- Technological Innovation: Advances in battery storage, hybrid systems, and digital monitoring improve reliability and efficiency.
Conclusion: The Solar Opportunity
Africa’s solar revolution is more than just an energy story—it’s a pathway to economic empowerment, climate resilience, and inclusive growth. With the right financial structures, stakeholder alignment, and commitment to execution, solar power can light the way forward.
🌍 Are you a developer, investor, or policymaker looking to enhance your solar project pipeline? Reach out to Finteam for tailored financial models and strategic insights that drive impact and bankability.